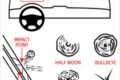
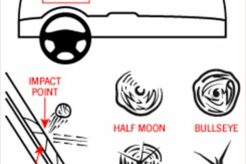
April 24, 2024
0 comment
Hobbs Farm Equipment Inc. is a leading provider of high-quality agricultural machinery and equipment. With a wide...

Boost Your Farm’s Efficiency with Hobbs Farm Equipment
April 23, 2024
0 comment
Latest Posts

April 25, 2024
0 comment
Wondering why Jake from State Farm was replaced? Find out the real reason behind the change in...

Unveiling Animal Farm’s True Leader: Identifying the Characters Who Assume Leadership Roles
February 10, 2024
0 comment
The characters in Animal Farm who display leadership qualities are Napoleon and Snowball, as they both strive...
State Farm Account Disabled: Factors Affecting Duration and How to Reactivate
April 25, 2024
0 comment
Wondering how long State Farm disables accounts? Find out here! Learn about the process and steps you...

State Farm Account Disabled: Factors Affecting Duration and How to Reactivate
April 25, 2024
0 comment
Wondering how long State Farm disables accounts? Find out here! Learn about the process and steps you...