April 18, 2024
0 comment
Explore our wide range of farm equipment toys for kids. These realistic and durable toys allow children...

Unveiling the Best Farm Equipment at Tulare, CA Show!
April 17, 2024
0 comment
Latest Posts

April 18, 2024
0 comment
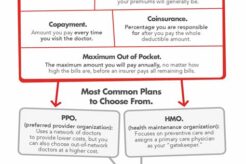
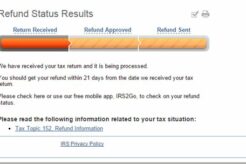
State Farm is stepping up to help during the pandemic by offering financial assistance, supporting local communities,...

Gear Up for Fun: Explore Farm Equipment Toys!
April 18, 2024
0 comment

Unveiling Animal Farm’s True Leader: Identifying the Characters Who Assume Leadership Roles
February 10, 2024
0 comment
The characters in Animal Farm who display leadership qualities are Napoleon and Snowball, as they both strive...