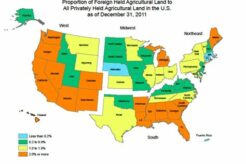
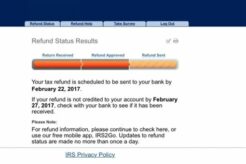
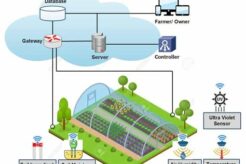
April 19, 2024
0 comment
Farming Equipment Companies specialize in providing various types of machinery and tools for agricultural purposes. These companies...

Unearth Unbeatable Deals at Farm Equipment Auctions!
April 19, 2024
0 comment
Latest Posts
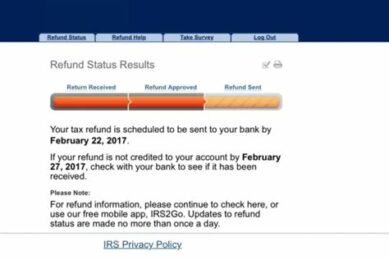
April 19, 2024
0 comment
Find out how State Farm is refunding money to policyholders during the COVID-19 pandemic and what you...

Revolutionize Your Farm: Top Farm Equipment Companies
April 19, 2024
0 comment

Unveiling Animal Farm’s True Leader: Identifying the Characters Who Assume Leadership Roles
February 10, 2024
0 comment
The characters in Animal Farm who display leadership qualities are Napoleon and Snowball, as they both strive...